| Table of Contents |
|---|
...
| maxLevel | 6 |
|---|
Overview
Data capture requires the provision of immutable fields that are generated deterministically in order to capture and store collected data inputs. Immutable Data capture items are identified by passive identifiers.
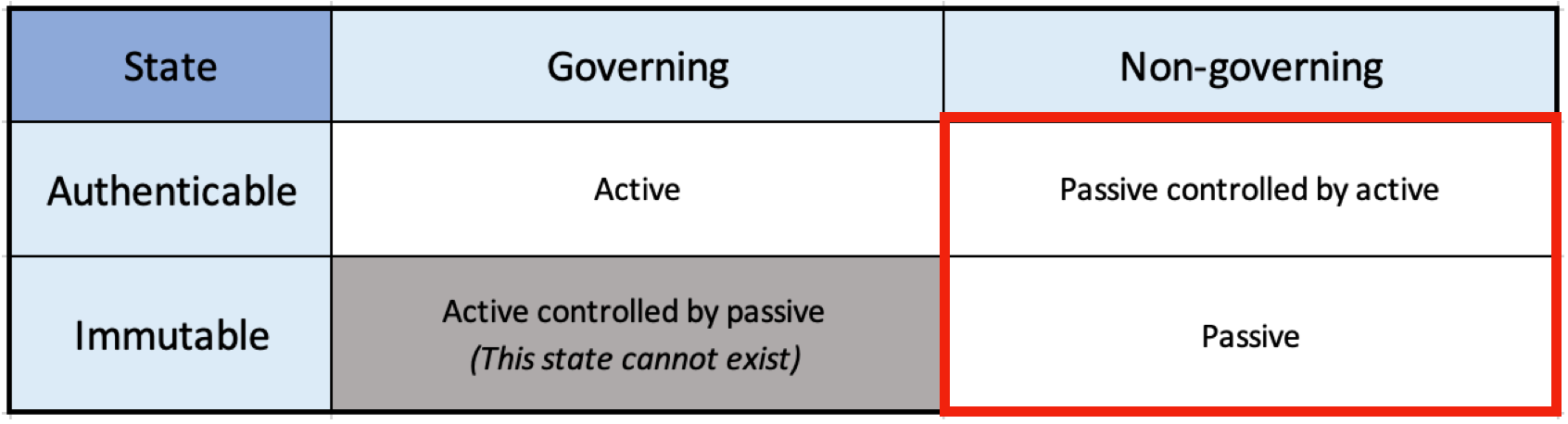
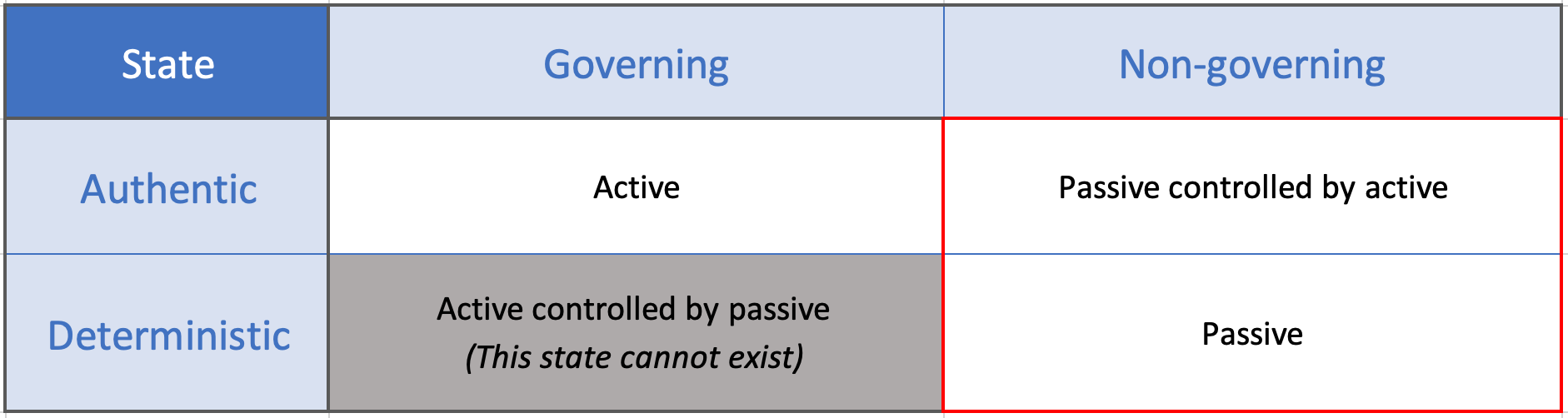
Table: A hash grid table describing the different states of of active and passive identifiers. The two states of passive identifiers are highlighted.
What is a Passive identifier?
An immutable identifier used that is generated deterministically to identify a non-governing entity, an inanimate object, or a static data inputitem. A passive identifier can either be (1) controlled by an active identifier or (2) not controlled.
...
The figure shows an instance when the DID subject may not be the same as the DID controller. In this scenario, the subject may represent a passive non-governing entity, an inanimate object or a static data input item with the controller’s DIDs being active, requiring a signing key for identity authentication. Through the authentication process, the controller is able to express ownership, control, or management of the passive resource.
- Uncontrolled passive identifier
An immutable A passive identifier that does not require any form of ownership, control, or management.
...
Passive identifier types include:
Resource Self-addressing identifier
An identifier that contains a cryptographic hash of digital content. Any change to the binary state of a single byte of the digital content will invalidate the hash. A hash value is an immutable fingerprint for digital content.is deterministically generated from and embedded in the content it identifies, making it and its data mutually tamper-evident.
Linking identifier (p/p-linkage)
An identifier that has an association with a cryptographic hash of digital content that can be used for linking information across a number of objects, applications, and/or systems. A linking identifier can be referenced in multiple locations and, as such, changing any single reference of the linking identifier should propagate throughout the daisy chain. As a linking identifier tends to be governed, this threading property works well for data revocation where a governing entity has the capability of revoking all data associated with the linking identifier.
...
Passive identifiers are assigned to the Semantic domain. Technical requirements include:
...